Cumidava (castra)
| Cumidava | |
|---|---|
 Ruins of the Northeastern gate (2013) | |
| Known also as | Castra of Râșnov |
| Founded | 2nd century AD |
| Place in the Roman world | |
| Province | Dacia Superior, Dacia Apulensis |
| Limes | Transalutanus |
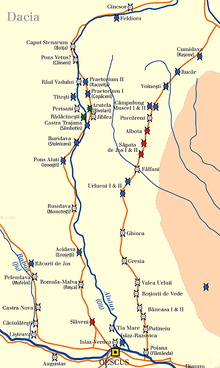
| Directly connected to | Castra of Drumul Carului, Castra of Brașov-Șprenghi |
| Structure | |
| — Stone structure — | |
| Construction technique | Opus incertum |
| — Wood and earth structure — | |
| Size and area | 114 m × 110 m ( ha) |
| Stationed military units | |
| — Cohorts — | |
| VI Nova Cumidavensium Alexandrina[1] | |
| Location | |
| Coordinates | 45°37′07″N 25°26′30″E / 45.618707°N 25.441580°E |
| Altitude | 608 m (1,995 ft) |
| Place name | Grădişte,[2] Erdenburg, Eulenburg, Orlenburg |
| Town | Râșnov |
| County | Brașov |
| Site notes | |
| Discovery year | 1856 [2] |
| Condition | Ruined |
| Excavation dates | 1939, 1969 - 1970 |
| Archaeologists | M. J. Ackner, Mihail Macrea, Constantin Daicoviciu[2] |
Cumidava was a fort in the Roman province of Dacia Apulensis. It is located at 4 km (2.5 mi) northwest of the city Râșnov, Romania near the city of Vulcan. The site is located on the middle terrace of Bârsa River.
It was part of the Roman frontier system of the Limes Transalutanus and was in a strategic position to the north of the Rucăr–Bran Pass.
It was a large fort sufficient for a milliaria or quingenaria equitata cohort.
Several overlapping forts from different phases have been found. The earliest wooden and earth fort from the time of Trajan measured 110x114 m surrounded by a 10 m wide and 2 m high earth mound and defensive ditch of depth 2 m on the NW and SW sides.[3] The second construction phase was a stone fort of 118×124 m with the porta praetoria on the NE side and walls 1.5-1.7 m thick. On the NE and SE sides the wall was laid in the ditch of the wood and earth phase, the ditch behind being filled with the bank of the earth and wood phase. On the NE and SE sides were three defensive ditches of 5×1.75 m; 5.50×1.25 m and 1.65×0.80 m, while on the SW side two trenches (3×1.25 m; 2.80×1 m), and a single trench on the NW side.[4] This phase dates to the later reign of Hadrian or the beginning of Antoninus Pius.
In 2016, as part of the LIMES National Program, geophysical surveys revealed a smaller fort (castellum) about 40 m east of the large fort and approximately 73×50 m, predating the stone fort. Approximately 78 m NNE of the stone fort a building consisting of two rooms with a semicircular apse oriented to the NW was found.

Garrison[edit]
It was occupied by only two cohorts Vindelicorum Cumidavensis (cohors IV and cohors IV Nova)[5] who had taken the name Cumidava (Komidava of Ptolemy)[6][7][8] as testified by an inscription found in the fort. The IV Vindelicorum, a peditata quingenaria cohort, was moved from Arzbach to Râșnov sometime in the beginning of the 3rd century and built a similar fort to that at Arzbach judging by the unusual character of the ancillary buildings inside.[9] Notably the headquarters building has a length-to-width ratio is reversed in relation to that of the fort, and there is a narrow courtyard, similar to the one at Râșnov.
Inscriptions[edit]
An inscription from 3rd century AD dedicated to Iulia Mamea was found here:[10]
See also[edit]
Notes[edit]
- ^ Istoria României, Transilvania, Volumul I, Capitolul II - Etnogeneza românilor, de Dr. Ioan Glodariu Archived 2012-03-28 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ a b c Raport științific privind derularea proiectului Strategii defensive și politici transfrontaliere. Integrarea spațiului Dunării de Jos în civilizația romană (STRATEG)
- ^ Marcu, The fort at Râșnov (Cumidava) and the Cohors Vindelicorum, Acta Musei Napocensis, 55, 2018 I: 205-226
- ^ Petculescu et al. Râșnov, jud. Brașov [Cumidava]. Punct: Grădiște, Erdenburg, Cronica Cercetărilor Arheologice; 2018
- ^ Dumitru Protase, Istoria Romanilor: Daco-Romani, Romanici, Algeni, Academia Româna, Secția de Științe Istorice și Arheologie, Editura Enciclopedică, 2001,
- ^ L'Année épigraphique: revue des publications épigraphiques relatives a l'antiquité romaine, Académie des inscriptions & belles-lettres (France) Presses Universitaires de France., 1968
- ^ Dapper 2009, p. 223.
- ^ Treptow & Bolovan 1996, p. 35.
- ^ Marcu, The fort at Râșnov (Cumidava) and the Cohors Vindelicorum, Acta Musei Napocensis, 55, 2018 I: 205-226
- ^ Pintilie, Alin-Sebastian. "Castrul roman Cumidava". Archived from the original on 2016-04-08. Retrieved 2013-05-06.
Works cited[edit]
- Dapper, Morgan De (2009). Ol' Man River: Geo-archaeological Aspects of Rivers and River Plains. Academia Press. ISBN 978-90-382-1404-7.
- Treptow, Kurt W.; Bolovan, Ioan (1996). Treptow, Kurt W.; Bolovan, Ioan (eds.). A History of Romania. East European Monographs. ISBN 978-0-88033-345-0.
External links[edit]
 Media related to Castra Cumidava at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to Castra Cumidava at Wikimedia Commons- Roman castra from Romania - Google Maps / Earth Archived 2012-12-05 at archive.today